第2课数据结构_分类
热度🔥:95 免费课程
授课语音
数据结构分类
1. 介绍
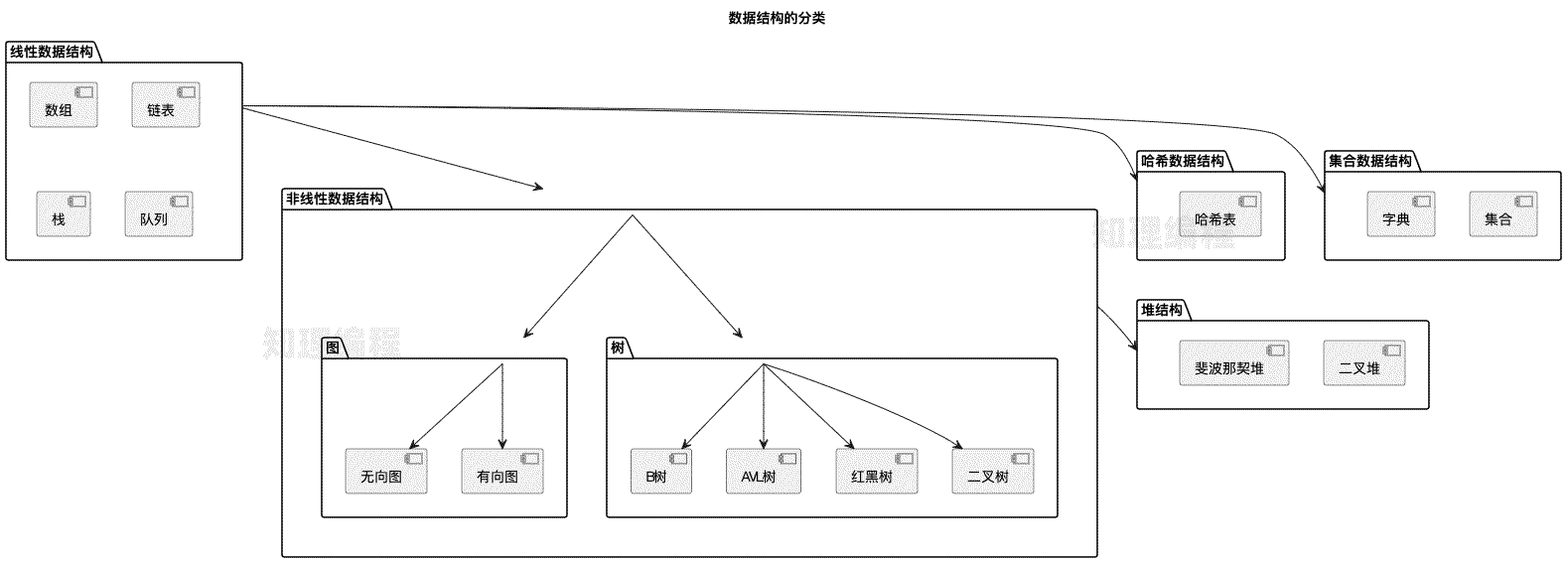
常见的数据结构包括数组、链表、栈、队列、哈希表、树、堆和图,分为逻辑结构和物理结构。
1.1 逻辑结构
逻辑结构描述了数据之间的关系和组织方式,主要分为线性结构和非线性结构。
线性结构
线性结构中的数据元素按顺序排列,每个元素有且只有一个前驱和一个后继。主要包括:
数组(Array):一组相同类型的元素,按顺序存储在内存中。支持随机访问,但插入和删除操作较慢,因为可能需要移动大量元素。
链表(Linked List):由一系列节点组成,每个节点包含数据和指向下一个节点的指针。链表的变体包括:
- 单链表(Singly Linked List):每个节点只有一个指针,指向下一个节点。
- 双链表(Doubly Linked List):每个节点有两个指针,分别指向前一个节点和下一个节点。
- 循环链表(Circular Linked List):链表的尾节点指向头节点,形成一个环。
栈(Stack):遵循“后进先出”(LIFO)原则的数据结构。主要操作有推入(push)和弹出(pop)。
队列(Queue):遵循“先进先出”(FIFO)原则的数据结构。主要操作有入队(enqueue)和出队(dequeue)。它的变体包括:
- 双端队列(Deque):可以在两端进行插入和删除操作的队列。
- 优先队列(Priority Queue):每个元素都有一个优先级,按照优先级顺序进行操作。
非线性结构
非线性结构中的数据元素没有线性排列的顺序,元素间的关系更加复杂。主要包括:
树(Tree):一种分层的数据结构,包含节点和边。每个节点可以有零个或多个子节点。常见的树结构包括:
二叉树(Binary Tree):每个节点最多有两个子节点(左子节点和右子节点)。
- 完全二叉树(Complete Binary Tree):除了最后一层外,每层的节点都完全填满,最后一层的节点从左到右依次填充。
- 满二叉树(Full Binary Tree):每个节点要么是叶子节点,要么有两个子节点。
- 平衡二叉树(Balanced Binary Tree):每个节点的左右子树的高度差不超过某个阈值(通常为1)。
二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree, BST):二叉树的一种,其中左子树的值小于根节点的值,右子树的值大于根节点的值。
- AVL平衡树(Balanced Tree):自平衡的二叉搜索树,任意节点的左右子树高度差不超过1。
- 红黑树(Red-Black Tree):自平衡的二叉搜索树,节点颜色限制。
B树(B Tree):自平衡的多路搜索树,适合存储和检索。每个节点可以有多个子节点,每个节点包含多个键(keys)和子节点指针。
B+树(B+ Tree):B树的变体,所有键值都存储在叶子节点中,内部节点仅存索引。
堆(Heap):一种特殊的完全二叉树,用于实现优先队列。分为最大堆(根节点最大)和最小堆(根节点最小)。
图(Graph):由节点(顶点)和连接节点的边组成的结构。图可以是:
- 无向图(Undirected Graph):边没有方向,连接两个节点。
- 有向图(Directed Graph):边有方向,从一个节点指向另一个节点。
- 加权图(Weighted Graph):边有权值,表示连接的代价或距离。
- 无权图(Unweighted Graph):边没有权值,只有连接关系。
哈希表 是一种非常重要的数据结构,用于实现高效的插入、删除和查找操作。它通过哈希函数将数据映射到数组中的特定位置,以便在常数时间内完成这些操作。
图示
1.2 物理结构
物理结构描述了数据如何在计算机内存中实际存储。主要分为内存连续结构和内存分散结构。
内存连续结构:数据在内存中是连续存储的。主要包括:
- 数组(Array):数据元素在内存中连续存储,支持快速随机访问。
内存分散结构:数据在内存中不是连续存储的,而是通过指针或引用连接起来。主要包括:
- 链表(Linked List):节点在内存中分散存储,每个节点包含数据和指向下一个节点的指针(或双向链表中还包含指向前一个节点的指针)。
所有的数据结构都是基于数组、链表或两者的组合实现的。
2. 代码案例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// ====================== 线性结构 ===========================
// 1. 数组(Array)类
class ArrayStructure
{
private int size; // 数组大小
private List<int> array; // 数组数据
// 构造函数,初始化数组
public ArrayStructure(int size)
{
this.size = size;
array = new List<int>(new int[size]); // 初始化数组,默认值为 0
}
// 设置指定索引的值
public void Set(int index, int value)
{
if (index >= 0 && index < size)
{
array[index] = value;
}
else
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("Index out of bounds"); // 索引越界错误
}
}
// 获取指定索引的值
public int Get(int index)
{
if (index >= 0 && index < size)
{
return array[index];
}
else
{
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("Index out of bounds"); // 索引越界错误
}
}
// 打印数组内容
public void Print()
{
foreach (var item in array)
{
Console.Write(item + " "); // 输出数组元素
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// 2. 链表(Linked List)
// 2.1 单链表(Singly Linked List)节点类
class Node
{
public int Data; // 节点数据
public Node Next; // 指向下一个节点的指针
public Node(int data)
{
Data = data;
Next = null;
}
}
// 单链表(Singly Linked List)类
class SinglyLinkedList
{
private Node head; // 链表头节点
public SinglyLinkedList()
{
head = null; // 初始化空链表
}
// 向链表末尾添加新节点
public void Append(int data)
{
Node newNode = new Node(data); // 创建新节点
if (head == null)
{
head = newNode; // 如果链表为空,直接将头指针指向新节点
}
else
{
Node last = head;
while (last.Next != null) // 找到链表的最后一个节点
{
last = last.Next;
}
last.Next = newNode; // 将最后一个节点的指针指向新节点
}
}
// 打印链表内容
public void Print()
{
Node current = head;
while (current != null) // 遍历链表
{
Console.Write(current.Data + " -> "); // 输出节点数据
current = current.Next;
}
Console.WriteLine("None"); // 输出链表结束标志
}
}
// 2.2 双链表(Doubly Linked List)节点类
class DoublyNode
{
public int Data; // 节点数据
public DoublyNode Next; // 指向下一个节点的指针
public DoublyNode Prev; // 指向前一个节点的指针
public DoublyNode(int data)
{
Data = data;
Next = null;
Prev = null;
}
}
// 双链表(Doubly Linked List)类
class DoublyLinkedList
{
private DoublyNode head; // 双链表头节点
public DoublyLinkedList()
{
head = null; // 初始化空链表
}
// 向双链表末尾添加新节点
public void Append(int data)
{
DoublyNode newNode = new DoublyNode(data); // 创建新节点
if (head == null)
{
head = newNode; // 如果链表为空,将头指针指向新节点
}
else
{
DoublyNode last = head;
while (last.Next != null) // 找到链表的最后一个节点
{
last = last.Next;
}
last.Next = newNode; // 将最后一个节点的指针指向新节点
newNode.Prev = last; // 设置新节点的前向指针
}
}
// 打印双链表内容
public void Print()
{
DoublyNode current = head;
while (current != null) // 遍历双链表
{
Console.Write(current.Data + " <-> "); // 输出节点数据
current = current.Next;
}
Console.WriteLine("None"); // 输出链表结束标志
}
}
// 2.3 循环链表(Circular Linked List)节点类
class CircularNode
{
public int Data; // 节点数据
public CircularNode Next; // 指向下一个节点的指针
public CircularNode(int data)
{
Data = data;
Next = null;
}
}
// 循环链表(Circular Linked List)类
class CircularLinkedList
{
private CircularNode head; // 循环链表头节点
public CircularLinkedList()
{
head = null; // 初始化空链表
}
// 向循环链表末尾添加新节点
public void Append(int data)
{
CircularNode newNode = new CircularNode(data); // 创建新节点
if (head == null)
{
head = newNode; // 如果链表为空,将头指针指向新节点
newNode.Next = newNode; // 新节点的 next 指向自己,形成循环
}
else
{
CircularNode last = head;
while (last.Next != head) // 找到链表的最后一个节点
{
last = last.Next;
}
last.Next = newNode; // 将最后一个节点的 next 指向新节点
newNode.Next = head; // 新节点的 next 指向头节点,完成循环
}
}
// 打印循环链表内容
public void Print()
{
if (head == null) // 如果链表为空
{
Console.WriteLine("Empty List");
return;
}
CircularNode current = head;
do // 遍历循环链表
{
Console.Write(current.Data + " -> "); // 输出节点数据
current = current.Next;
} while (current != head); // 循环直到回到头节点
Console.WriteLine("(back to head)"); // 输出回到头节点的标志
}
}
// 3. 栈(Stack)类
class Stack
{
private List<int> items; // 栈内存储的元素
public Stack()
{
items = new List<int>();
}
// 压栈操作
public void Push(int item)
{
items.Add(item);
}
// 弹栈操作
public int Pop()
{
if (IsEmpty())
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("pop from empty stack"); // 栈空时弹栈错误
}
int top = items[items.Count - 1]; // 获取栈顶元素
items.RemoveAt(items.Count - 1); // 弹出栈顶元素
return top;
}
// 查看栈顶元素
public int Peek()
{
if (IsEmpty())
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("peek from empty stack"); // 栈空时查看栈顶错误
}
return items[items.Count - 1]; // 返回栈顶元素
}
// 判断栈是否为空
public bool IsEmpty()
{
return items.Count == 0;
}
// 获取栈的大小
public int Size()
{
return items.Count;
}
}
// 4. 队列(Queue)类
class Queue
{
private List<int> items; // 队列内存储的元素
public Queue()
{
items = new List<int>();
}
// 入队操作
public void Enqueue(int item)
{
items.Add(item);
}
// 出队操作
public int Dequeue()
{
if (IsEmpty())
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("dequeue from empty queue"); // 队列空时出队错误
}
int front = items[0]; // 获取队首元素
items.RemoveAt(0); // 移除队首元素
return front;
}
// 判断队列是否为空
public bool IsEmpty()
{
return items.Count == 0;
}
// 获取队列的大小
public int Size()
{
return items.Count;
}
}
// ====================== 非线性结构 ===========================
// 1. 二叉树(Binary Tree)节点类
class TreeNode
{
public int Data; // 节点数据
public TreeNode Left; // 左子节点
public TreeNode Right; // 右子节点
public TreeNode(int data)
{
Data = data;
Left = null;
Right = null;
}
}
// 二叉树(Binary Tree)类
class BinaryTree
{
private TreeNode root; // 根节点
public BinaryTree()
{
root = null; // 初始化为空树
}
// 插入节点
public void Insert(int data)
{
root = InsertRec(root, data); // 从根节点开始插入
}
// 递归插入节点
private TreeNode InsertRec(TreeNode node, int data)
{
if (node == null)
{
return new TreeNode(data); // 如果节点为空,创建新节点
}
if (data < node.Data)
{
node.Left = InsertRec(node.Left, data); // 如果数据小于当前节点,递归插入左子树
}
else
{
node.Right = InsertRec(node.Right, data); // 如果数据大于当前节点,递归插入右子树
}
return node;
}
// 中序遍历
public void Inorder()
{
InorderRec(root); // 从根节点开始中序遍历
Console.WriteLine();
}
// 递归中序遍历
private void InorderRec(TreeNode node)
{
if (node != null)
{
InorderRec(node.Left); // 遍历左子树
Console.Write(node.Data + " "); // 输出节点数据
InorderRec(node.Right); // 遍历右子树
}
}
}
// 2. 堆(Heap)类
class MinHeap
{
private List<int> heap; // 存储堆元素
public MinHeap()
{
heap = new List<int>();
}
// 向上调整堆
private void HeapifyUp(int index)
{
while (index > 0)
{
int parent = (index - 1) / 2;
if (heap[index] < heap[parent])
{
Swap(index, parent); // 如果当前元素小于父节点,交换
index = parent; // 更新当前索引
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
// 向下调整堆
private void HeapifyDown(int index)
{
int leftChild = 2 * index + 1;
int rightChild = 2 * index + 2;
int smallest = index;
if (leftChild < heap.Count && heap[leftChild] < heap[smallest])
{
smallest = leftChild; // 左子节点更小
}
if (rightChild < heap.Count && heap[rightChild] < heap[smallest])
{
smallest = rightChild; // 右子节点更小
}
if (smallest != index)
{
Swap(index, smallest); // 交换当前节点与最小子节点
HeapifyDown(smallest); // 继续调整
}
}
// 交换堆中两个元素的位置
private void Swap(int i, int j)
{
int temp = heap[i];
heap[i] = heap[j];
heap[j] = temp;
}
// 插入元素
public void Insert(int value)
{
heap.Add(value); // 将元素添加到堆末尾
HeapifyUp(heap.Count - 1); // 调整堆
}
// 删除最小元素
public int ExtractMin()
{
if (heap.Count == 0)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("Heap is empty"); // 堆为空错误
}
int minValue = heap[0]; // 获取最小值
heap[0] = heap[heap.Count - 1]; // 将堆尾元素移到堆顶
heap.RemoveAt(heap.Count - 1); // 移除堆尾元素
HeapifyDown(0); // 调整堆
return minValue;
}
}
// 3. 图(Graph)类
class Graph
{
private Dictionary<int, List<int>> adjList; // 图的邻接表表示
public Graph()
{
adjList = new Dictionary<int, List<int>>();
}
// 添加边
public void AddEdge(int u, int v)
{
if (!adjList.ContainsKey(u))
{
adjList[u] = new List<int>();
}
if (!adjList.ContainsKey(v))
{
adjList[v] = new List<int>();
}
adjList[u].Add(v); // 添加 u -> v 边
adjList[v].Add(u); // 添加 v -> u 边(无向图)
}
// 打印图的邻接表
public void PrintGraph()
{
foreach (var pair in adjList)
{
Console.Write(pair.Key + " -> ");
foreach (var neighbor in pair.Value)
{
Console.Write(neighbor + " "); // 输出邻接节点
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
// 主程序,测试各种数据结构
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// ====================== 测试数组 =======================
ArrayStructure arr = new ArrayStructure(5);
arr.Set(0, 10);
arr.Set(1, 20);
arr.Print();
// ====================== 测试单链表 =======================
SinglyLinkedList sll = new SinglyLinkedList();
sll.Append(1);
sll.Append(2);
sll.Append(3);
sll.Print();
// ====================== 测试栈 =======================
Stack stack = new Stack();
stack.Push(10);
stack.Push(20);
Console.WriteLine(stack.Pop());
// ====================== 测试队列 =======================
Queue queue = new Queue();
queue.Enqueue(1);
queue.Enqueue(2);
Console.WriteLine(queue.Dequeue());
// ====================== 测试二叉树 =======================
BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree();
bt.Insert(5);
bt.Insert(3);
bt.Insert(7);
bt.Inorder();
// ====================== 测试堆 =======================
MinHeap minHeap = new MinHeap();
minHeap.Insert(3);
minHeap.Insert(1);
Console.WriteLine(minHeap.ExtractMin());
// ====================== 测试图 =======================
Graph g = new Graph();
g.AddEdge(1, 2);
g.AddEdge(1, 3);
g.PrintGraph();
}
}
解释:
- C# 中的类、构造函数和方法的定义与 C++ 稍有不同。
- C# 使用
List<int>来替代std::vector<int>,并处理了相应的插入、删除等方法。 - 方法名和成员变量在 C# 中遵循更严格的命名约定(例如首字母大写)。
- 异常处理改为使用
InvalidOperationException或ArgumentOutOfRangeException。
3. 总结
本文概述了常见的数据结构及其分类,分别介绍了逻辑结构和物理结构,并通过代码示例展示了各种数据结构的基本实现。掌握这些数据结构将有助于高效地处理和存储数据。












