第1课java_IO模型
热度🔥:59 免费课程
授课语音
Java的IO模型
1. 介绍
Java的I/O(输入/输出)指的是数据交换的过程,比如文件读写、网络通信等。
基本概念
- 流(Streams) 是对数据的一种抽象,分为输入和输出流,用于数据的读取和写入,包括:
- 字节流(用于处理非文本数据)
- 字符流(用于处理文本数据)
- 通道(Channel) 是Java NIO/AIO中的组件,能够直接操作文件、网络连接等,包括:
- 文件通道(如
FileChannel)用于文件操作 - 网络通道(如
SocketChannel、ServerSocketChannel)用于网络通信 - 通道是双向的,可以同时进行读写操作
- 文件通道(如
- 选择器(Selector) 是Java NIO中的组件,用于监视通道的I/O事件。
- 缓冲区(Buffer) 提供了一种高效的数据读写方式,提升I/O性能,包括:
- 字节缓冲区(
ByteBuffer) - 字符缓冲区(
CharBuffer) - 其他类型的缓冲区(如
IntBuffer、LongBuffer等)
- 字节缓冲区(
同步与异步
- 同步 指操作按严格顺序执行,调用者会被阻塞,直到I/O操作完成,才能继续下一个请求。
- 异步 指操作不按严格顺序执行,调用者不会被阻塞,I/O操作完成时会通过回调通知。
阻塞与非阻塞
- 阻塞 I/O操作期间,线程被挂起,直到操作完成,无法执行其他任务。
- 非阻塞 操作不挂起,线程可以继续执行其他任务,操作完成后通过回调进行通知。
三种I/O模型
- BIO(阻塞I/O):每个I/O连接都有一个独立线程,线程等待I/O操作完成,不能执行其他任务。
- NIO(非阻塞I/O):主要提高I/O操作效率,适用于高并发场景。
- 使用缓冲区(
Buffer)读写数据。 - 应用多路复用机制,选择器(
Selector)管理多个通道(Channel),实现单线程处理多个连接。 - 通过读取通道数据到缓冲区,写入缓冲区数据到通道。
- 使用缓冲区(
- AIO(异步I/O):也是非阻塞I/O。
- I/O操作完成后,通过回调通知应用程序实现异步处理。
- 核心组件包括异步通道(
AsynchronousChannel)和完成处理器(CompletionHandler),比NIO进一步提升I/O效率,但编程复杂度较高,并可能在不同操作系统上表现不一。
图示
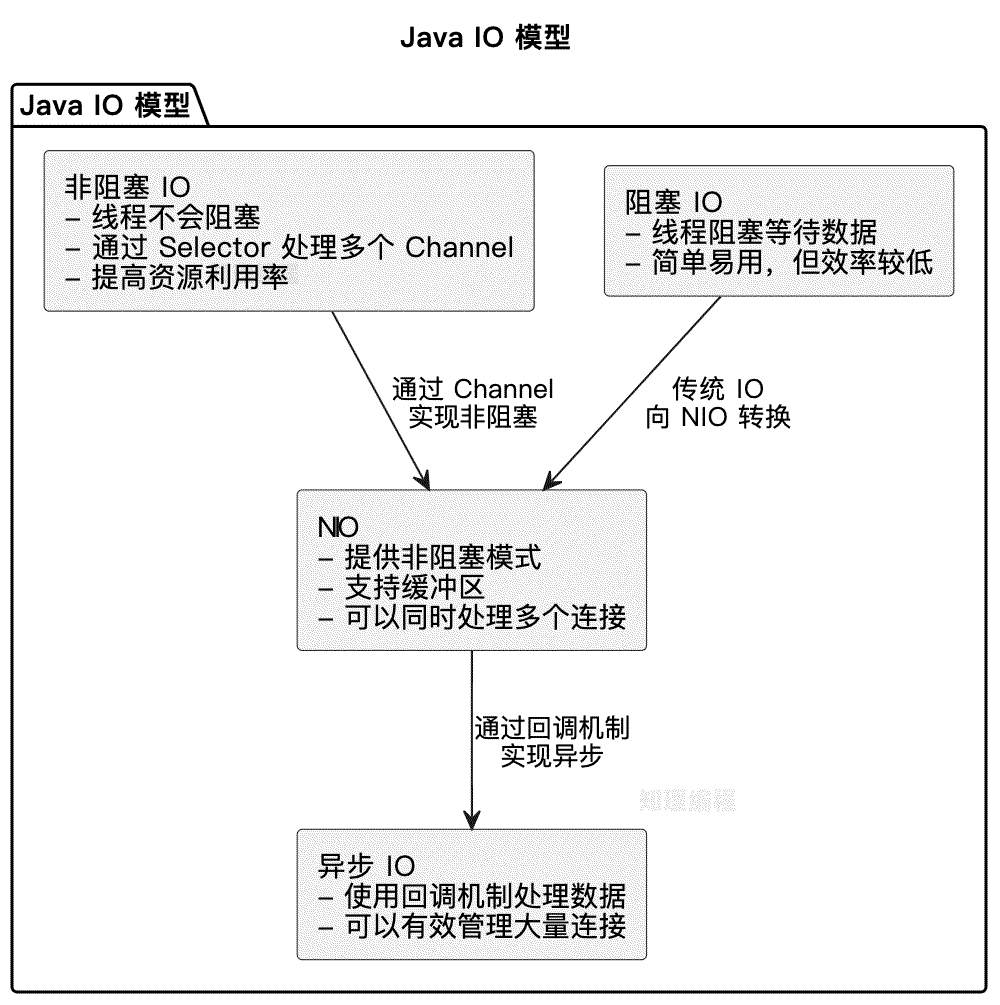
I/O最佳实践
- 及时关闭资源,确保流和通道在使用完成后及时关闭。
- 使用缓冲区,减少I/O操作次数,提升性能。
- 注意编解码问题,处理字符流时应关注字符编码。
- 考虑线程安全问题,例如多线程访问同一通道资源时,需进行线程同步。
2. 代码案例
简单的(客户端-服务端)消息通信系统
BIO服务器
package com.zhilitech.bio;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class BioServer {
private static final int PORT = 1234; // 服务器监听的端口
private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = 5; // 核心线程数
private static final int MAX_POOL_SIZE = 10; // 最大线程数
private static final int KEEP_ALIVE_TIME = 60; // 线程空闲时间(秒)
private static final int QUEUE_CAPACITY = 100; // 任务队列容量
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建自定义线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
CORE_POOL_SIZE,
MAX_POOL_SIZE,
KEEP_ALIVE_TIME,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(QUEUE_CAPACITY)
);
try (ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(PORT)) {
System.out.println("服务器启动,等待客户端连接...");
while (true) {
// 阻塞,等待客户端连接
Socket clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("客户端连接成功");
// 提交任务到线程池处理客户端请求
threadPool.execute(() -> handleClient(clientSocket));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown(); // 关闭线程池
}
}
private static void handleClient(Socket clientSocket) {
try (InputStream inputStream = clientSocket.getInputStream();
OutputStream outputStream = clientSocket.getOutputStream()) {
// 读取客户端发送的数据
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int bytesRead = inputStream.read(buffer);
System.out.println("接收到客户端的数据: " + new String(buffer, 0, bytesRead));
// 将读取到的数据返回给客户端
outputStream.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
clientSocket.close(); // 关闭客户端连接
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
BIO客户端
package com.zhilitech.bio;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
public class BioClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 连接到服务器
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 1234);
// 获取输出流,发送数据到服务器
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("Hello, BIO Server!".getBytes());
// 获取输入流,读取服务器返回的数据
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int bytesRead = inputStream.read(buffer);
// 打印服务器返回的数据
System.out.println("从服务器接收到的数据: " + new String(buffer, 0, bytesRead));
// 关闭连接
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
NIO服务器
package com.zhilitech.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class NioServer {
private static final int PORT = 1234; // 服务器监听的端口
private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = 5; // 核心线程数
private static final int MAX_POOL_SIZE = 10; // 最大线程数
private static final int KEEP_ALIVE_TIME = 60; // 线程空闲时间(秒)
private static final int QUEUE_CAPACITY = 100; // 任务队列容量
private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 256; // 缓冲区大小
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建自定义线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
CORE_POOL_SIZE,
MAX_POOL_SIZE,
KEEP_ALIVE_TIME,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(QUEUE_CAPACITY)
);
try {
// 打开ServerSocketChannel并绑定端口
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.bind(new java.net.InetSocketAddress(PORT));
// 设置为非阻塞模式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 打开Selector并注册ServerSocketChannel
Selector selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("服务器启动,等待客户端连接...");
while (true) {
// 等待多个通道上的事件,处理I/O操作
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
// 处理新连接
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel clientChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
clientChannel.configureBlocking(false);
clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println("客户端连接成功");
}
// 处理读事件
if (key.isReadable()) {
// 使用线程池处理读取操作
threadPool.execute(() -> handleClient(key));
}
keyIterator.remove(); // 移除当前处理的选择键
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown(); // 关闭线程池
}
}
private static void handleClient(SelectionKey key) {
SocketChannel clientChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
if (!clientChannel.isConnected()) {
System.out.println("客户端已关闭");
return;
}
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(256); // 创建缓冲区
try {
int bytesRead = clientChannel.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead > 0) {
buffer.flip(); // 切换到读取模式
String message = new String(buffer.array(), 0, bytesRead);
System.out.println("来自客户端的消息: " + message);
// 回应客户端
buffer.clear(); // 清空缓冲区
buffer.put(("" + message).getBytes()); // 写入响应数据
buffer.flip(); // 切换到写入模式
clientChannel.write(buffer); // 发送给客户端
} else if (bytesRead == -1) {
// 客户端关闭连接
closeChannel(key);
System.out.println("客户端连接关闭");
}
} catch (ClosedChannelException e) {
System.out.println("客户端连接关闭异常");
closeChannel(key);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IO异常");
closeChannel(key);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void closeChannel(SelectionKey key) {
try {
if (key != null && key.channel() != null) {
key.channel().close(); // 关闭通道
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("关闭通道异常: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
NIO客户端
package com.zhilitech.nio;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class NioClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 创建一个SocketChannel并设置为非阻塞模式
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 连接到服务器
socketChannel.connect(new java.net.InetSocketAddress("localhost", 1234));
// 发送消息
String message = "你好,NIO服务器!";
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(message.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
socketChannel.write(buffer); // 发送数据到服务器
// 清空缓冲区并准备读取响应
buffer.clear();
int bytesRead;
// 接收服务端响应
buffer.clear();
bytesRead = socketChannel.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead > 0) {
buffer.flip(); // 切换到读取模式
String response = new String(buffer.array(), 0, bytesRead);
System.out.println("服务器响应: " + response);
}
Thread.sleep(3000); // 等待3秒以观察输出
// 关闭连接
socketChannel.close();
}
}
AIO服务器
package com.zhilitech.aio;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class AioServer {
private static final int PORT = 1234; // 服务器监听的端口
private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = 5; // 核心线程数
private static final int MAX_POOL_SIZE = 10; // 最大线程数
private static final int KEEP_ALIVE_TIME = 60; // 线程空闲时间(秒)
private static final int QUEUE_CAPACITY = 100; // 任务队列容量
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 创建自定义线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
CORE_POOL_SIZE,
MAX_POOL_SIZE,
KEEP_ALIVE_TIME,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(QUEUE_CAPACITY)
);
try (AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open()) {
serverSocketChannel.bind(new java.net.InetSocketAddress(PORT));
System.out.println("AIO服务器启动,等待客户端连接...");
// 异步接受客户端连接
serverSocketChannel.accept(null, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Void>() {
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel, Void attachment) {
System.out.println("客户端连接成功");
// 继续接受其他客户端连接
serverSocketChannel.accept(null, this);
// 使用线程池处理客户端数据
threadPool.execute(() -> handleClient(clientChannel));
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Void attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 保持主线程活跃一段时间
Thread.sleep(10000);
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown(); // 关闭线程池
}
}
private static void handleClient(AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel) {
if (!clientChannel.isOpen()) {
System.out.println("客户端已关闭");
return;
}
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); // 创建缓冲区
clientChannel.read(buffer, buffer, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer buffer) {
buffer.flip(); // 切换到读取模式
clientChannel.write(buffer); // 将数据返回给客户端
buffer.clear(); // 清空缓冲区
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer buffer) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
AIO客户端
package com.zhilitech.aio;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class AioClient {
private static final String SERVER_ADDRESS = "localhost"; // 服务器地址
private static final int PORT = 1234; // 服务器端口
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try (AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open()) {
// 连接到服务器
Future<Void> future = socketChannel.connect(new java.net.InetSocketAddress(SERVER_ADDRESS, PORT));
future.get(); // 等待连接完成
// 发送数据到服务器
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap("你好, AIO 服务器!".getBytes());
Future<Integer> writeFuture = socketChannel.write(buffer);
writeFuture.get(); // 等待写入完成
// 读取服务器返回的数据
buffer.clear();
Future<Integer> readFuture = socketChannel.read(buffer);
readFuture.get(); // 等待读取完成
buffer.flip(); // 切换到读取模式
System.out.println("从服务器接收到的数据: " + new String(buffer.array(), 0, buffer.limit()));
Thread.sleep(1000); // 等待1秒
}
}
}
以上代码展示了BIO、NIO和AIO三种I/O模型的基本用法,通过这些示例可以了解不同I/O模型的工作原理和使用场景。










