第2课java_零拷贝
热度🔥:44 免费课程
授课语音
Java的零拷贝
1. 介绍
零拷贝是一种提高网络数据传输效率的技术,旨在减少数据在不同系统组件(如内核空间和用户空间)之间的复制次数。这种技术不仅可以降低CPU负载,还能减少时延,从而提升整体性能。零拷贝技术主要应用于大文件传输、高性能网络应用服务和文件服务器等场景。
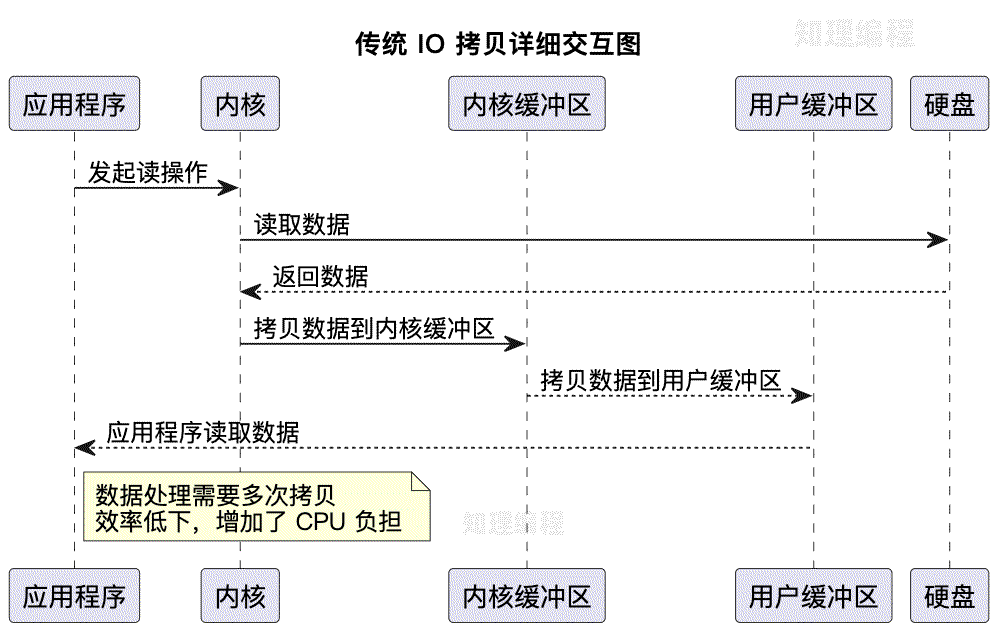
传统IO操作
在传统的I/O操作中,数据的处理过程存在多次复制和用户态与内核态之间的切换,这导致性能瓶颈。具体过程如下:
- 应用程序发起读操作。
- 内核将数据从硬盘或外部存储设备读取并拷贝到内核缓冲区。
- 数据再从内核缓冲区拷贝到用户缓冲区。
- 应用程序从用户缓冲区读取数据进行处理。
这种方式不仅效率低下,还增加了CPU的负担。
图示
零拷贝
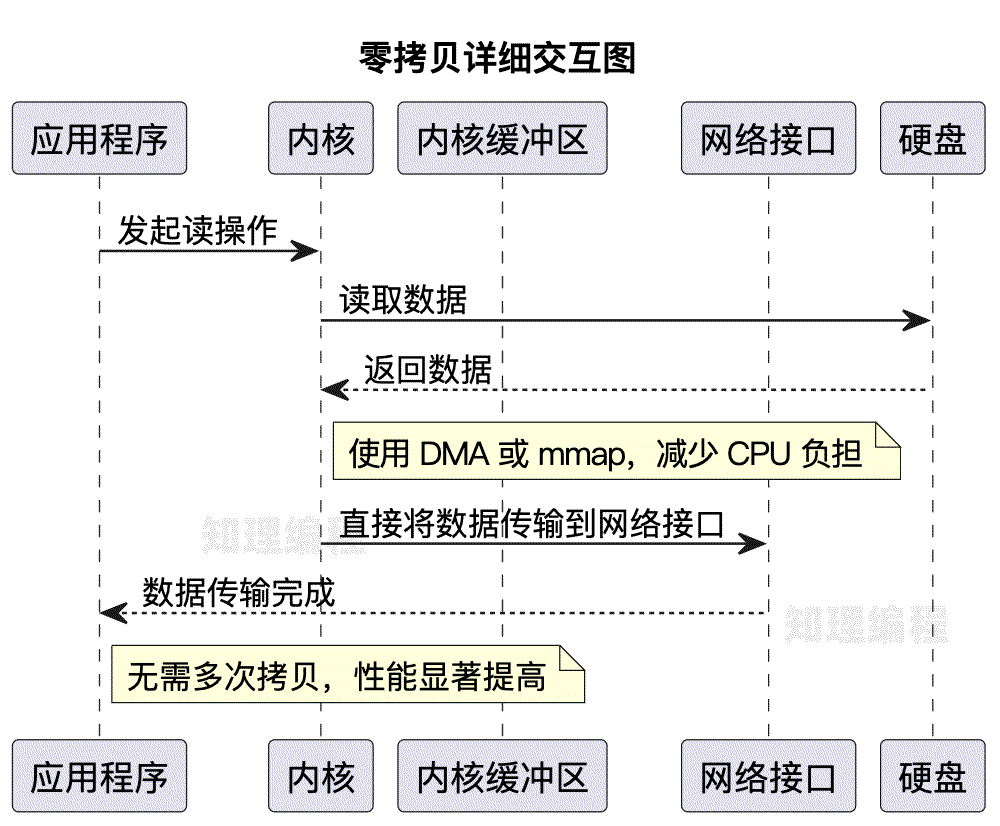
零拷贝通过减少拷贝次数和用户态与内核态的切换来提高性能。实现零拷贝的方法主要有以下几种:
- DMA(直接内存访问):数据可以直接在设备和内存之间传输,无需经过CPU,这样可以显著减少CPU的计算负担。
- 内存映射(mmap):应用程序可以直接访问文件系统中的数据,而无需将数据拷贝到用户态的缓冲区。
- sendfile系统调用:在网络传输中,将文件数据直接从文件系统传输到网络接口,避免了经过用户空间的步骤。
图示
Java具体实现
在Java中,零拷贝的具体实现方式包括:
FileChannel的transferTo和transferFrom方法:transferTo可以将FileChannel通道中的数据直接传输到SocketChannel,而transferFrom则反向操作。这些方法减少了用户态和内核态之间的切换。MappedByteBuffer:通过FileChannel的map方法,将文件内容直接映射到内存中,进而实现高效的读写操作。sendfile系统调用:底层通过FileChannel和SocketChannel来实现文件的零拷贝传输。
2. 代码案例
基于FileChannel的代码案例
以下代码展示了如何使用FileChannel实现零拷贝的服务器和客户端。
服务器代码
package com.zhilitech.zerocopy;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption;
public class ZeroCopyServer {
private static final int PORT = 8888;
private static final String FILE_PATH = "largefile.txt"; // 需要传输的文件
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get(FILE_PATH), StandardOpenOption.READ)) {
// 绑定服务器到指定端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new java.net.InetSocketAddress(PORT));
System.out.println("Server started on port " + PORT);
while (true) {
try (SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept()) {
System.out.println("Client connected");
// 将文件内容传输到客户端
long position = 0; // 当前读取的位置
long size = fileChannel.size(); // 文件总大小
while (position < size) {
// 使用零拷贝技术,将数据直接传输到客户端
position += fileChannel.transferTo(position, size - position, socketChannel);
}
System.out.println("File sent successfully");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
客户端代码
package com.zhilitech.zerocopy;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption;
public class ZeroCopyClient {
private static final String SERVER_ADDRESS = "localhost"; // 服务器地址
private static final int SERVER_PORT = 8888; // 服务器端口
private static final String OUTPUT_FILE_PATH = "fromserver_largefile.txt"; // 保存的文件路径
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new java.net.InetSocketAddress(SERVER_ADDRESS, SERVER_PORT));
FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get(OUTPUT_FILE_PATH), StandardOpenOption.CREATE, StandardOpenOption.WRITE)) {
System.out.println("Connected to server");
// 将数据从SocketChannel读取到FileChannel
long position = 0; // 当前写入的位置
long size;
while ((size = fileChannel.transferFrom(socketChannel, position, Long.MAX_VALUE)) > 0) {
position += size; // 更新写入位置
}
System.out.println("File received and saved successfully");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
ByteBuffer和allocateDirect直接内存
下面的代码演示了如何使用直接内存的ByteBuffer来实现零拷贝的服务器和客户端。
直接内存服务器代码
package com.zhilitech.zerocopy;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class NioDirectBufferServer {
private static final int PORT = 8888; // 监听的端口号
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open()) {
// 绑定到指定端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new java.net.InetSocketAddress(PORT));
System.out.println("Server started on port " + PORT);
// 定义要发送的数据
String data = "Hello, this is a zero-copy message with direct buffer!";
// 创建直接内存的 ByteBuffer,减少JVM堆内存与操作系统之间的复制
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(data.length());
// 将数据写入缓冲区
buffer.put(data.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
// 切换到读取模式
buffer.flip();
while (true) {
try (SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept()) {
System.out.println("Client connected");
// 发送数据到客户端
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
socketChannel.write(buffer);
}
// 重新设置缓冲区,以便下一个客户端重复使用,提高性能
buffer.rewind();
System.out.println("Message sent successfully");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
直接内存客户端代码
package com.zhilitech.zerocopy;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class NioDirectBufferClient {
private static final String SERVER_ADDRESS = "localhost"; // 服务器地址
private static final int SERVER_PORT = 8888; // 服务器端口号
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new java.net.InetSocketAddress(SERVER_ADDRESS, SERVER_PORT))) {
System.out.println("Connected to server");
// 创建直接内存的 ByteBuffer,用于接收数据
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
StringBuilder message = new StringBuilder();
// 从服务器读取数据
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = socketChannel.read(buffer)) > 0) {
buffer.flip(); // 切换到读取模式
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
message.append((char) buffer.get());
}
buffer.clear(); // 清空缓冲区以便下一次读取
}
System.out.println("Message received: " + message);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这些代码示例展示了如何利用Java的零拷贝技术来实现高效的数据传输,特别是在处理大文件和高并发的网络请求时,可以显著提高性能。希望这些内容能帮助大家更好地理解零拷贝的原理和实现方式。










